A report released by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2022 has indicated that we have reached critical tipping points in terms of irreversible climate change. The message is clear: urgent action must be taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in order to safeguard our planet and ensure the long-term sustainability of our ecosystem.
While there is a general consensus on the need to reverse the conditions leading to these tipping points, many businesses face significant challenges in reducing their carbon footprint and adopting more sustainable practices. Surprisingly, software development is often overlooked as a potential contributor to the problem.
However, the concept of green software engineering, also known as green coding, green computing, or sustainable software, has been gaining traction in recent years. It emphasizes the importance of minimizing environmental damage through efficient and effective software engineering, attracting interest from architects, developers, and coders who want to make a meaningful, long-term contribution to saving the planet.
In this article, we will explore the emerging concepts and principles that underpin green software engineering. We will delve into the best measurement tools available, examine a model that provides a comprehensive understanding of sustainable software development, and highlight the three emissions scopes defined by the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP).
What Exactly Is Green Software Engineering?
Green software engineering is a design concept that advocates for software to be developed and used in a manner that has minimal to no impact on the environment. It encompasses all aspects of a software product's lifecycle, including its design and use as well as economic, social, and ecological impacts. By adhering to green coding principles, software engineers can play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and improving sustainability across businesses of all sizes.
The Principles of Green Coding
Traditionally, sustainable software development focused primarily on cost, speed, and agility, rather than considering its potential to minimize emissions and enhance sustainability. However, there has been a recent surge in efforts to establish a global set of principles and standards for green software development. The Green Software Foundation, a non-profit organization founded in 2021, has spearheaded this movement by developing eight fundamental principles to guide software engineers in their approach to development. These principles are:
- Carbon: Build applications that are carbon efficient.
- Electricity: Build applications that are energy efficient.
- Carbon Intensity: Consume electricity with the lowest carbon intensity.
- Embodied Carbon: Build applications that are hardware efficient.
- Energy Proportionality: Maximize the energy efficiency of hardware.
- Networking: Reduce the amount of data and distance it must travel across the network.
- Demand Shaping: Build carbon-aware applications.
- Measurement & Optimization: Focus on step-by-step optimizations that increase overall carbon efficiency.
To delve further into each principle, refer to this resource.
The Philosophies of Green Software Engineering
The principles of green coding are underpinned by two key philosophies:
- Everyone has a part to play in the climate solution: Everything is interconnected, and small changes can lead to significant outcomes.
- Sustainability is enough to justify our work: Sustainable applications are not only environmentally friendly but can also be cost-effective, high-performing, and resilient.
Measures and Models for Green and Sustainable Software Development
When it comes to measuring green and sustainable software practices, there is no one-size-fits-all approach or tool. It is crucial to select metrics that align with your organization's sustainability targets. Here are two approaches to consider:
- Understanding Your Environmental Impact in the Cloud
Major cloud providers offer tools and dashboards to help identify and visualize the impact of the services consumed through their platforms. While these tools are important, they primarily focus on the resources used by software workloads; they do not provide a comprehensive measurement of green software development or the complete sustainability assessment of a software product.
- Using Sustainability Dimensions to Measure Software's Greenness
A valuable model discussed in the paper 'Green measurements for software products based on sustainability dimensions' offers a broader understanding of software sustainability. This model incorporates social, economic, and environmental factors, providing a more holistic view of a software ecosystem's impact.
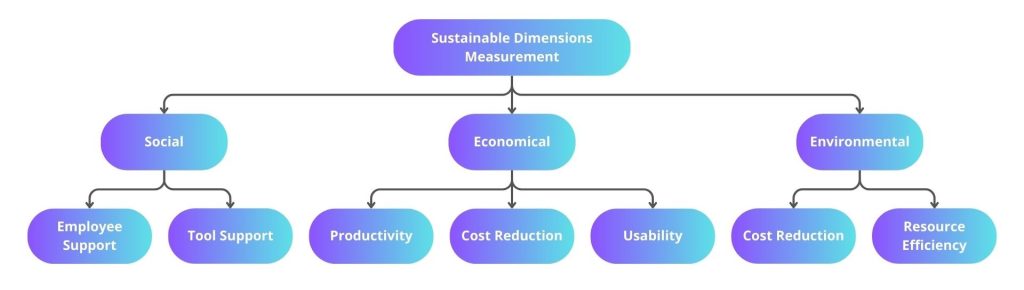
- Measuring Emissions Using the Greenhouse Gas Protocol Framework
Measuring the carbon footprint of software presents challenges due to the many variables involved throughout the lifecycle. However, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP) provides a standardized framework for measuring, accounting for, and reporting emissions. The GHGP categorizes emissions into three scopes:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from sources owned or controlled by a company.
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased energy generation.
- Scope 3: Indirect emissions occurring outside of Scopes 1 and 2 in the value chain, including upstream and downstream emissions.
While software development typically contributes more emissions through Scope 3, it is important to recognize that every aspect of the development process can play a role in reducing emissions.
Check out a related article:
Business in Times of Crisis – The Intersog Way
Considerations and Challenges
It is essential to approach the shift towards green and sustainable software development with caution. Going green may involve additional costs, and finding a balance between sustainability and affordability is crucial. Additionally, many IT systems still rely on carbon-intensive energy sources due to their cost-effectiveness.
To prioritize green and sustainable software development, a change in mindset is required. Small changes and adaptations made over time can have a significant and lasting impact. Development teams can start by incorporating green thinking into their ways of working.
Four Ways to Achieve Greener Ways of Working
- Green Thinking: Infuse green thinking and practices into all aspects of software delivery, considering the team's impact on the environment and promoting sustainability in daily activities.
- Measure and Monitor: Estimate and track the sustainability of each feature throughout its journey, ensuring that sustainability is considered from the early design and development phases through production.
- Automate: Leverage automation to streamline processes and minimize resource consumption, such as spinning up and shutting down environments and cleaning up code repositories.
- Be Mindful: Recognize that everyone shares the responsibility for greener ways of working, and promote a culture of sustainability throughout the organization.
In Conclusion
The threat of irreversible climate change demands our serious attention. Green software engineering and sustainable software development offer effective strategies to make a meaningful impact on our society and the environment. By adopting the eight principles of green coding and initiating discussions within development teams, we can contribute to creating a more sustainable planet for future generations. Let us embrace the small changes that can drive a better future.
Leave a Comment