Launching a startup comes with its fair share of uncertainty - will your product find its place in the market? How can you deliver value in a way that customers are willing to pay for? For most startups, answering these questions is key to long-term viability and attracting investor interest.
Before diving into product development, it's important to work out how your startup will generate revenue. In other words, you need a solid business model. This article will guide you through the process of designing a business model tailored to your startup's unique needs.
Understanding the Business Model
A business model is the blueprint for how your company generates revenue. It’s more than just a plan - it’s a structured approach to creating, delivering, and capturing value. A well-crafted business model stems from a deep understanding of your customers, their pain points, and the unique solutions your business provides. By aligning your value proposition with a sound operational strategy and an optimized cost structure, you set the foundation for long-term success and profitability.
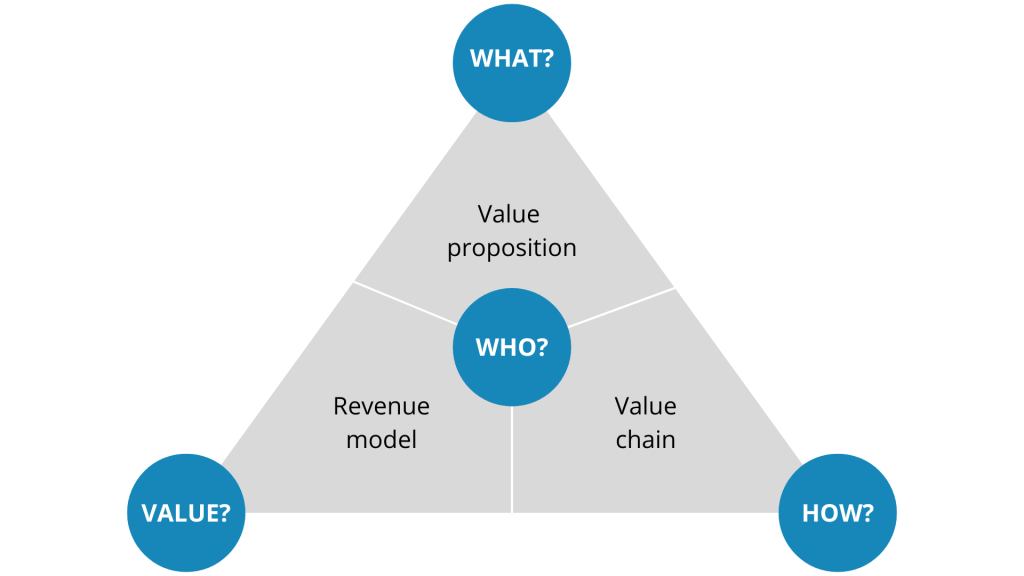
The Four Pillars of a Business Model (Gassmann’s Framework)
A strong business model is built on four fundamental dimensions:
To bring these concepts together, many startups use a structured tool called a business model canvas.
Business model canvas: A Strategic Blueprint
- WHO: Who are your target customers and what are their key needs?
- WHAT: What is your core value proposition - what unique value does your product or service offer?
- HOW: How will you deliver this value using your organisation's resources and capabilities?
- VALUE: How will you capture value through your pricing and revenue model?
Originally introduced by Alexander Osterwalder and Dr Yves Pigneur in Business Model Generation, the business model canvas is a visual framework that helps companies design, test and refine their strategies. For start-ups, this tool simplifies complex business planning and provides a clear roadmap for achieving product-market fit and long-term success.
The Business model canvas allows founders to take a step back and assess their startup from a strategic perspective. By mapping out key elements such as revenue streams, customer segments and operational logistics, startups gain insight into market positioning and potential growth opportunities.
When Should You Use a Business Model Canvas?
A business model canvas isn’t just for startups - it’s a powerful tool for any business looking to refine its strategy. Consider using it when:
- You’re building a new business model - It helps you visualize the most critical elements of your strategy, ensuring a strong foundation.
- You need to understand the competition - You can map competitors’ business models to spot their strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
- You want to improve an existing business - By analyzing customer needs and market shifts, you can pivot or refine your strategy for better results.
Why Does the Business Model Canvas Matter?
Here’s why startups and established companies alike swear by it:
- Identifies essential resources – Helps you pinpoint what’s required to build and deliver your product.
- Exposes opportunity gaps – Reveals market needs you may have overlooked.
- Improves competitive analysis – Allows you to deconstruct rivals’ models and find ways to differentiate.
- Attracts investors – Provides a concise, clear way to showcase business potential.
- Drives innovation – Encourages thinking outside the box to refine offerings.
- Supports business agility – Maps out potential changes and adaptations.
- Enables rapid testing – Helps evaluate different business models efficiently.
- Aligns team efforts – Ensures that goals, resources, and actions are in sync.
- Puts customers at the center – Helps shape a business around customer needs and market demand.
What Does The Model Consist Of
The business model canvas is built around nine key components, which fall into three main categories:
- Market & Customers (Right Side): Defines customer segments, relationships, and channels.
- Internal Business Factors (Left Side): Covers key activities, resources, and partnerships.
- Value Proposition & Revenue (Center & Bottom): Highlights how your business creates, delivers, and captures value.
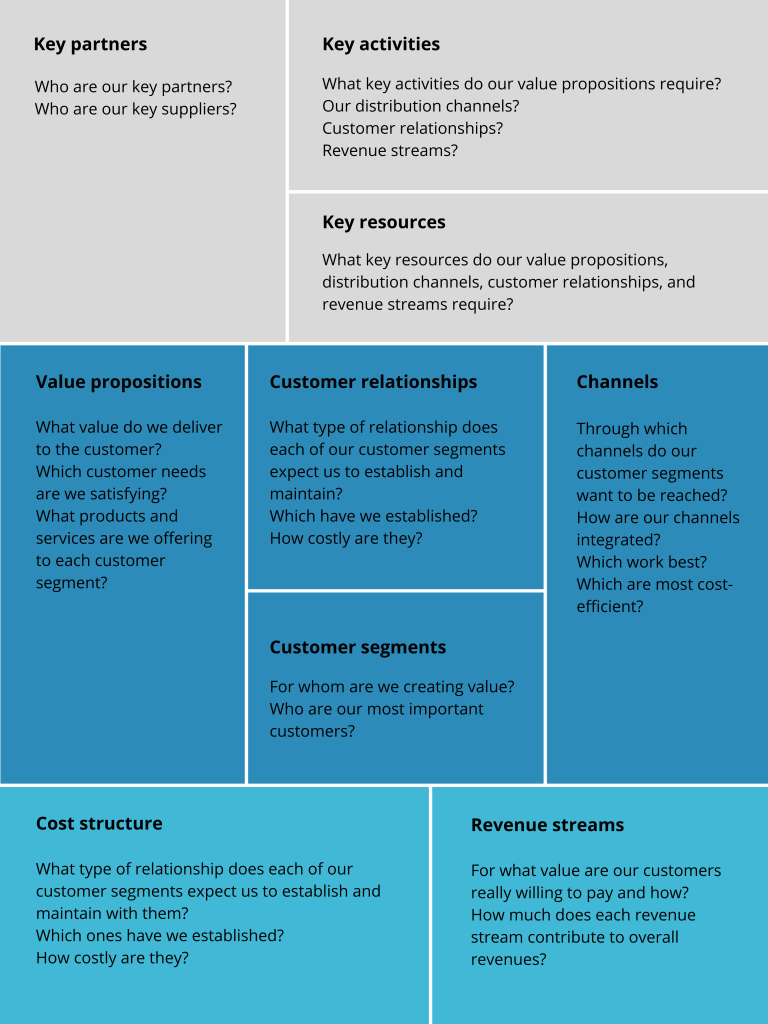
By condensing an entire business model into a single-page visual map, startups gain an agile, adaptable alternative to traditional business plans. Before launching a product, you can use the business model canvas to define your strategy. As your business evolves, it remains a living document - allowing you to pivot, refine, and optimize for growth.
How to Design a Winning Business Model Using a Canvas
Step 1: Identify Your Customer Segments
The foundation of any business model is knowing WHO you’re serving. When filling out your business model canvas, the first step is defining your customer segments - the groups of people or businesses that will benefit from your product. Their needs, behaviors, and expectations will influence every strategic decision you make.
Before diving in, consider what kind of market you’re targeting:
- Mass Market – Broad, unspecialized audience with similar needs (e.g., smartphone users).
- Niche Market – Specific customer groups with tailored needs (e.g., luxury watch collectors).
- Segmented Market – Different but related customer groups requiring variations in service (e.g., banks catering to both high-net-worth clients and everyday customers).
- Diversified Market – Serving multiple, unrelated customer groups (e.g., Amazon selling both retail products and cloud services).
- Multi-Sided Market – Two or more interdependent customer groups (e.g., credit card companies serving both cardholders and merchants).
Once you define your market type, segment your customers based on demographics, behaviors, and pain points. This is where an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) comes in - a blueprint of your perfect customer who would get the most value from your product.
Next, refine this further with a buyer persona, a detailed representation of the individuals who will actually make purchasing decisions. Understanding these personas helps shape customer-focused messaging across your entire business strategy.
Step 2: Craft Your Value Proposition
Your value proposition is the reason customers choose you over competitors - it’s the unique benefit they can’t find elsewhere. Each customer segment will have different expectations, so your value proposition should align with their specific needs.
Value can be:
- Quantitative – Price, speed, cost-efficiency, delivery terms
- Qualitative – Design, user experience, convenience, personalization
Some common value proposition elements include:
✔ Newness – A solution that didn’t exist before
✔ Performance – A product that works better than alternatives
✔ Convenience – Making life easier for the customer
✔ Personalization – Tailored experiences or offerings
✔ Cost Savings – Helping customers reduce expenses
✔ Risk Reduction – Minimizing uncertainty or potential downsides
✔ Brand & Status – A product that elevates the customer’s identity
To ensure a perfect fit between your product and market, use the Value Proposition Canvas, which breaks customer needs into three categories:
🔹 Gains – The benefits customers want to experience
🔹 Pains – The problems they want to eliminate
🔹 Customer Jobs – The tasks they’re trying to accomplish
Then, map out how your product delivers value:
🔹 Gain Creators – How your product enhances the customer’s life
🔹 Pain Relievers – How it removes obstacles and frustrations
🔹 Products & Services – The specific features that deliver value
Prioritize these elements based on what matters most to your customers. A strong product-market fit happens when your offering directly addresses the biggest customer pains and delivers meaningful benefits.
Step 3: Define Your Channels
Think of channels as the bridges connecting your business to your customers. They serve two key functions: delivering your value proposition and helping customers discover your product. Essentially, they dictate how your offering enters the market and how buyers enter your sales pipeline.
You have several channel options, each with its pros and cons:
- Direct channels – Your own website, in-house sales teams, or direct outreach. These give you more control and higher margins but can be expensive to maintain.
- Indirect channels – Physical retail locations owned by your company. These expand reach but add logistical complexity.
- Partner channels – Third-party retailers, wholesale distributors, or partner websites. These can amplify product visibility but come with lower profit margins.
Choosing the Right Channel Mix
Partner channels are particularly useful for getting your brand in front of a broader audience - especially for startups looking to establish themselves. Early-stage businesses often rely on word of mouth, social media, and app stores as primary distribution channels. While direct channels provide better margins, they require a bigger investment in infrastructure and marketing. The key is finding the right balance that maximizes reach without straining your resources.
Check out a related article:
Navigating the Modern Software Development Journey
Step 4: Mapping Customer Relationships
How do you plan to engage with your customers? Your relationship with them should align with their expectations, the nature of your product, and your business objectives. A well-defined approach can enhance loyalty, but it’s also important to weigh the cost of maintaining these relationships.
Here are the most common types of customer relationships:
- Personal assistant – A real human supports customers throughout their journey, from sales to post-purchase help (think iTunes support).
- Dedicated personal assistant – A more exclusive service where a single representative is assigned to a client (as seen in banking).
- Self-service – Customers have all the tools they need to navigate your product on their own.
- Automated services – A hybrid of self-service and automation, offering personalized recommendations and assistance (like Pandora’s music algorithms).
- Communities – A space for customers and company reps to engage, solve issues, and share insights. This not only builds trust but also provides valuable user feedback (GlaxoSmithKline fosters this approach).
- Co-creation – Customers actively contribute to product design and content creation (YouTube thrives on this model).
- Transactional – A one-time purchase with little to no direct interaction (like buying a snack from a vending machine).
Some businesses benefit from offering a mix of these options. For instance, a banking app may function as a self-service tool but still allow users to connect with a human representative when needed. When defining customer relationships, be sure to tailor them to each segment’s needs while balancing costs.
Step 5: Define Your Revenue Streams
Now that you've identified your customer segments, it's time to answer the big question: How will your business make money? Revenue streams define the ways your company generates income, and selecting the right ones is crucial for long-term sustainability.
To determine the best revenue model, consider:
- What are your customers willing to pay for? Understanding perceived value is key.
- How do they prefer to pay? One-time purchases, subscriptions, or pay-as-you-go models all have different appeal.
- What percentage of your total revenue comes from each source? Diversification can reduce risk.
Common Revenue Streams
Different businesses monetize their offerings in different ways. Here are some popular models:
- Asset sales – Selling full ownership of a product (e.g., buying a car).
- Usage fees – Charging based on product or service usage (e.g., cloud storage fees).
- Subscription fees – Granting time-based access for a recurring fee (e.g., Netflix).
- Leasing/renting – Allowing temporary use of an asset for a fee (e.g., car rentals).
- Licensing – Selling the rights to use intellectual property (e.g., software patents).
- Brokerage fees – Earning a commission for facilitating transactions (e.g., stock trading platforms).
- Advertising – Charging businesses to promote their products on your platform (e.g., Google Ads).
Beyond selecting revenue streams, you need to define your pricing model. This can be either fixed (set prices that don’t change) or dynamic (prices that adjust based on demand, market conditions, or negotiation).
- Fixed pricing is predictable and straightforward, making budgeting easier.
- Dynamic pricing adapts to real-time factors like inventory, time, or customer profile (e.g., airline tickets fluctuating based on demand).
The best revenue model is the one that maximizes profitability with minimal complexity. To build resilience, consider diversifying revenue streams—relying on just one can leave you vulnerable to market shifts.
Step 6: Identify Key Resources
Every business relies on critical assets to operate effectively. Your key resources are what enable you to develop your product, reach customers, maintain relationships, and ultimately generate revenue. These can be classified into four main categories:
- Physical assets – Tangible resources like factories, equipment, and retail stores.
- Intellectual property – Brands, patents, proprietary tech, or partnerships.
- Human resources – The people behind your business, from developers to sales teams.
- Financial assets – Cash flow, credit lines, and investment capital.
Your business model dictates which of these resources are most essential. A SaaS company, for example, relies heavily on intellectual and human capital, while a manufacturing business prioritizes physical assets.
Step 7: Define Key Activities
What are the essential actions your business must take to succeed? Key activities vary depending on your industry, but they generally fall into three main categories:
- Production – Creating and delivering products at the right scale and quality.
- Problem-solving – Addressing customer pain points through tailored solutions.
- Platform/network management – Maintaining and growing an ecosystem that connects users (e.g., a social media platform optimizing its algorithm).
For example:
- Microsoft focuses on software development.
- Dell is built around supply chain management.
- McKinsey & Co. thrives on problem-solving for clients.
Defining your key activities helps ensure your business is efficient, focused, and ready to scale.
Step 8: Establish Key Partnerships
No business operates in isolation. Strategic partnerships can help your startup optimize costs, reduce risks, and access essential resources. Identifying the right partners is crucial for scaling efficiently and staying competitive.
Types of Key Partnerships
- Strategic alliances with non-competitors – Collaborations that benefit both parties without direct competition (e.g., a fintech startup partnering with a cybersecurity firm).
- Cooperation between competitors – Industry players working together for mutual benefit (e.g., airlines in global alliances like Star Alliance).
- Joint ventures – Two or more companies pooling resources to create a new entity (e.g., Sony and Ericsson forming Sony Ericsson).
- Buyer–supplier relationships – Reliable suppliers ensure steady access to critical resources (e.g., Tesla’s partnerships with battery manufacturers).
Successful businesses thrive on well-structured partnerships. For instance:
- Facebook relies on content providers (news, music, and video distributors).
- Spotify partners with record labels rather than producing its own music.
- Airbnb collaborates with hosts while focusing on platform management.
The right partnerships can unlock new revenue opportunities, lower operational costs, and enhance product offerings.
Step 9: Define Your Cost Structure
A clear understanding of your startup’s costs is essential for financial sustainability. This step involves outlining all major expenses and balancing them with revenue projections.
Two Main Cost Approaches
- Value-driven cost structure – Prioritizes quality and differentiation over cost-cutting (e.g., luxury brands or premium tech products).
- Cost-driven cost structure – Focuses on efficiency and affordability, keeping expenses as low as possible (e.g., budget airlines).
Breaking Down Your Costs
Your cost structure consists of fixed and variable costs:
- Fixed costs – Expenses that remain unchanged regardless of production volume (e.g., salaries, rent, infrastructure).
- Variable costs – Expenses that fluctuate with business activity (e.g., raw materials, transaction fees).
Once you’ve defined the high-level categories, itemizing specific costs will help refine your financial strategy. The ultimate goal? Ensure projected revenue exceeds total costs - a key factor in designing a profitable, scalable business model.
Building Your Own Business Model Canvas
A fully completed business model canvas serves as a strategic tool for selecting the right business model for your startup. It provides clarity on your niche, core values, key resources, and essential activities needed to achieve your commercial objectives. Moreover, it enables you to refine your approach by turning assumptions into validated insights.
Steps to Effectively Use a Business Model Canvas
- Map out your business at a high level – Start by outlining the key elements: customer segments, value propositions, revenue streams, and cost structure.
- Link the canvas blocks – Every value proposition should align with a specific customer segment and corresponding revenue stream.
- Run validation tests – Test each assumption (e.g., product demand, pricing model) through market research, pilot programs, or customer feedback.
- Refine and iterate – Modify your canvas as you gain insights, optimizing elements based on real-world data.
- Use it continuously – The business model canvas isn’t just for startups. Established businesses should revisit and adapt their model as the market evolves.
Ready? Here’s an example for you:
Amazon’s Business Model Canvas
Amazon, the world’s largest e-commerce and cloud computing company, has a diversified business model spanning retail, technology, and logistics.
| Building Block | Amazon’s Approach |
| Customer Segments | Individual consumers, businesses, third-party sellers, enterprises (AWS users), Prime members. |
| Value Propositions | Wide product selection, fast & convenient delivery, competitive pricing, cloud computing services, Prime membership benefits. |
| Channels | Amazon website & mobile app, Alexa voice shopping, third-party seller platforms, AWS enterprise services. |
| Customer Relationships | AI-driven personalized recommendations, 24/7 customer support, Prime loyalty program, AWS account managers. |
| Revenue Streams | Product sales, subscription fees (Prime, Kindle Unlimited), AWS cloud services, advertising, third-party seller commissions. |
| Key Resources | E-commerce platform, cloud computing infrastructure, data analytics, fulfillment centers, AI and machine learning technology. |
| Key Activities | Online retail operations, logistics & supply chain management, software development, cloud computing services, AI-driven innovation. |
| Key Partnerships | Third-party sellers, logistics providers, payment processors, content creators (Prime Video, Audible). |
| Cost Structure | Fulfillment & delivery costs, cloud infrastructure investments, technology development (AI, ML), content licensing, marketing. |
Developing a business model canvas is an ongoing process that involves continuous analysis and research in each iteration until all critical aspects of your business model are clearly defined. One of its key advantages is its adaptability - even after your startup is launched, the canvas remains a valuable tool for refinement. Whenever market conditions shift or product improvements are needed, you can quickly update your business model to incorporate necessary changes.
If you need expert guidance in building and refining your business model or you need seasoned specialists to craft it into life, our team at Intersog is here to help. Let us help you navigate the complexities of business development - contact us today to get started.
Leave a Comment